Dna Replication Enzymes And Proteins

The mechanism of dna replication in eukaryotes is similar to dna replication in prokaryotic.
Dna replication enzymes and proteins. They are different proteins that copy genetic code to produce new cells. It occurs in three main stages: At the replication fork, many replication enzymes assemble on the dna into a complex molecular machine called the replisome.
Steps of dna replication in eukaryotes. Replication follows several steps that involve multiple proteins called replication enzymes and rna. In some instances, dna enzymes can also be used to repair or correct dna strands.
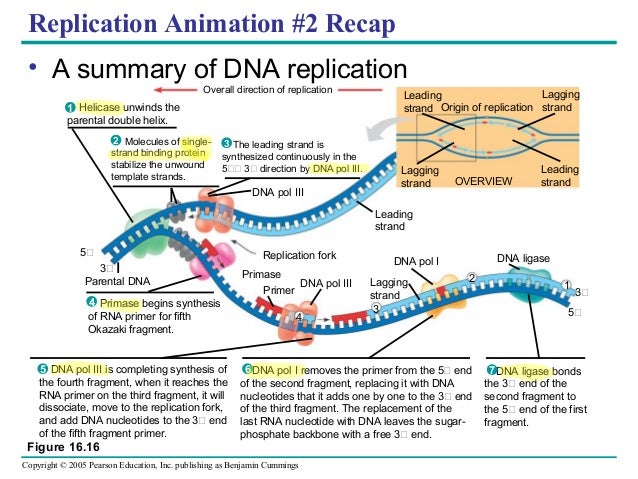
Leading and lagging strands and okazaki fragments. The enzymes recognize the incorrectly added nucleotide and excise it; An enzyme dna helicase unwinds the two strands by hydrolyzing the atp.
The replicated dna is present as long concatameric molecules (tandem repeats of the genome linked head. The synthesis of a dna molecule can be divided into three stages: There are many enzymes involved in dna replication due to the complex nature of the whole process.
Enzymes and proteins in dna replication 1. The process of dna replication begins at an origin of replication, where the molecule's two strands are separated, producing a replication bubble with two replication forks unzipping the dna bidirectionally away from the origin.prokaryotes usually have a single origin of replication for their single, circular dna. Herpesviruses code for several proteins, in addition to the dna polymerase, that are needed for dna replication.
In response to the molecular cues received during cell division, these molecules initiate dna replication, and synthesize two new strands using the existing strands as templates. Enzymes can be obtained to replicate dna strands artificially and are usually grouped into families. The dna replication in prokaryotes takes place in the following place: